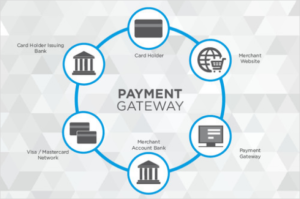
A payment gateway is a platform that allows any online business to accept payment. It can offer payment options like cards (debit and credit), digital wallets, UPI, and more. A payment gateway is what keeps the payments ecosystem rolling smoothly, as it enables online payments for consumers and businesses. If you’re an online merchant, you don’t need to be a payment gateway expert, but it’s worth understanding the basics of how an online payment flows from your customer to your bank account.The definition of a payment gateway is the technology that captures and transfers payment data from the customer to the acquirer and then transfers the payment acceptance or decline back to the customer. A payment gateway validates the customer’s card details securely, ensures the funds are available and eventually enables merchants to get paid. It acts as an interface between a merchant’s website and its acquirer. It encrypts sensitive credit card details, ensuring that information is passed securely from the customer to the acquiring bank, via the merchant.
In other words, the payment gateway works as the middleman between your customer and the merchant, ensuring the transaction is carried out securely and promptly. An online payment gateway can simplify how merchants integrate the necessary software. As the middleman during the payment processing, the gateway manages the customer’s sensitive card details between the acquirer and the merchant.
Now, these online businesses are known as merchants. They can range from eCommerce industries to any SaaS businesses.
Traditionally payment gateways in India were provided by banks in the early 90s. But, since the late 90s, private 3rd party corporations have entered the foray.
Today, most organizations integrate with these third-party payment processors to collect payments from their customers. Similarly, they can be used to disburse payments to vendors and employees. A payment gateway is a merchant service that processes credit card payments for e-commerce sites and traditional brick and mortar stores. Popular payment gateways include PayPal/Braintree, Stripe, and Square. Most payment gateways accomplish that in a few seconds with these steps:Encryption: Between the user’s browser and the server of the retailer, a payment gateway will encrypt (encode for private use) data for exclusive use between sellers and buyers. Request: The authorization request occurs when a payment processor gets approval from a credit card company or financial institution to proceed with the transaction.
Fulfillment: When the payment gateway has the authorization, it allows the website and interface to proceed to the next action.
Types of Payment Gateways
There are generally three types of payment gateways:
1. Redirects
Redirects might include an option for a PayPal payment, for example.
When the gateway takes a customer to a PayPal payment page to handle the complete transaction (i.e. processing and paying) it becomes a “Redirect.”
This has the advantage of simplicity for the retailer. A small business can use a Redirect gateway to incorporate the convenience and security of a major platform like PayPal, but the process also means less control for the merchant — and a second step for customers.
2. Checkout on-site, payment off-site.
Consider Stripe’s payment gateway: the front-end checkout will occur on your site, but the payment processing happens through Stripe’s back end.
Features
- Payment Gateway Services
- Fastest Merchant Approval
- Smooth integration across all platforms
- Start in minutes

